You need to find common factors in the equation. First, we factorise the denominator:
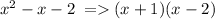
Which leaves is with the equation:
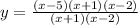
We can see that we have the common factors of (x+1) and (x-2), so these cancel out in the numerator and denominator:
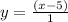
a.k.a: y = x - 5
So if x+1 and x-2 cancel out, then the x values of the holes are:
x+1=0
x= -1
And
x-2=0
x= 2
Now we plug in each of these numbers into our simplified equation:
y = x - 5
y=(-1)-5
y= -6
This gives us the coordinate (-1,-6)
y = x - 5
y=(2)-5
y= -3
This gives us the coordinate (2,-3)
So the holes are at (-1,-6) and (2,3)