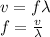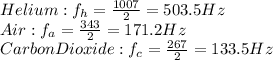The speed of sound is in the gas is given with this formula:
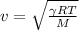
Where T is the temperature, M is the molar mass of the gas, R is universal gas constant and
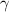
is heat capacity ratio.
We can find the speed of the sound in different gasses online ( you could also calculate it using above formula).
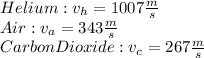
We know that pitch, wavelength, and speed of the sound are related:
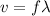
Because our wavelentgh is the same the frequency must be different.