Answer: The concentration of barium ions that must exceed to precipitate the salt is 0.245 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Solubility product is defined as the product of concentration of ions present in a solution each raised to the power its stoichiometric ratio. It is represented as
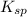
Barium fluoride is an ionic compound formed by the combination of 1 barium ion and 2 fluoride ions.
The equilibrium reaction for the ionization of barium fluoride follows the equation:
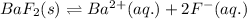
The solubility product for the above reaction is:
![K_(sp)=[Ba^(2+)]* [F^-]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/b7ach7v10tst5wtm42mwyoc2im8ntwc89s.png)
We are given:
![[F^-]=1.00* 10^(-2)M\\\\K_(sp)=2.45* 10^(-5)](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/lkg6767mvr174ko87euvumms9a9za1znq1.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![2.45* 10^(-5)=[Ba^(2+)]* (1.00* 10^(-2))^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/fm1dwtp70p86kh57i1cjaejyj96sf2mjsp.png)
![[Ba^(2+)]=(2.45* 10^(-5))/((1.00* 10^(-2))^2)=0.245M](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/chemistry/college/h4ogxcn2de92qbuh2r36syo02z4i01gjgi.png)
Hence, the concentration of barium ions that must exceed to precipitate the salt is 0.245 M