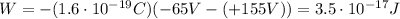The work done by the electric field is equal to the loss of electric potential energy of the proton in moving from its initial location to its final location:
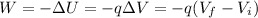
where
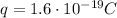
is the proton charge,
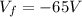
and
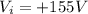
are the voltages in the final and initial locations. Substituting, we get