In order to solve the problem, let's write the equations of motion first. Let's take the x-axis as the horizontal direction, and the y-axis on the vertical direction (pointing downward). Calling
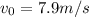
the initial velocity, and
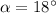
the angle below the horizontal, the equations of motion are
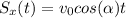
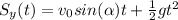
where
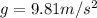
is the gravitational acceleration.
(a) To find the distance covered by the ball horizontally, we must simply calculate Sx at the time the ball hits the ground (t=4.0 s):
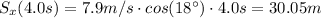
(b) The height from which the ball was thrown is the value of Sy at 4.0s, which is the distance covered by the ball before hitting the ground:
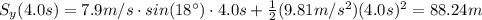
(c) To calculate how long does it take to the ball to reach 10.0 m below the initial point, we have to find the time at which Sy(t)=10.0 m. This means we must solve the following equation:
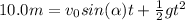
Using the data of the problem, we can solve this equation. We find two solutions for t: one is negative, so we can neglect it. The second one, which is the solution of the problem, is t=1.19 s.