Snell law basically says that when a ray of light crosses the interface between two different medium (for instance, from air to water), it changes direction following this relationship:
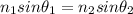
where n is the refraction index of the medium and
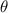
the angle of the ray with respect to the perpendicular to the interface.
A lens is usually built with a precise curvature, such that all the rays of light coming from outside are refracted inside the lens into a single point, called focal point. The path that the rays of light follow when crossing the interface between the air and the lens is given exactly by the Snell law.