Answer:
Explanation:
The congruence
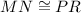 is false, because they are not corresponding sides.
is false, because they are not corresponding sides.
The corresponding sides are:
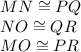
On the other hand, if
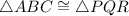 , then
, then
 .
.
We know that
 and
and
 , but they are equal, so
, but they are equal, so
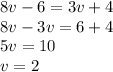
Then,
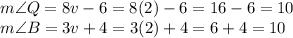
Therefore, those angles are equal to 10°.
In the second image, the given triangles have the following congruence:
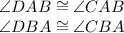
Also, they have side AB in common.
Therefore,
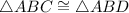 , by ASA.
, by ASA.