Answer:
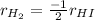
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, considering the given chemical reaction:
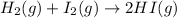
Thus, by applying the law of rate proportions, we can write:
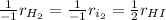
Whereas the stoichiometric coefficients of reactants are negative due their disappearance and that of the product is positive due to its appearance. In such a way, when we relate the rate of disappearance of hydrogen gas to the rate of formation of hydrogen iodide, we obtain:
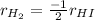
Best regards!