Answer:
(a)
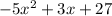
(b)
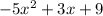
Explanation:
(a)
Let the polynomial be Q(x).
Given polynomial P(x) =
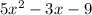
As per the given statement: A polynomial(Q(x)) which, when added to the polynomial
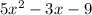 , is equivalent to 18.
, is equivalent to 18.
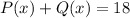
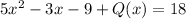
⇒
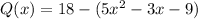
or
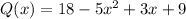
Simplify:
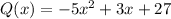
Therefore, the polynomial is,
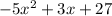
Check:
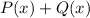 =
=
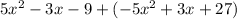
=
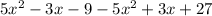
= 18
(b)
Let the polynomial be Q(x).
Given polynomial P(x) =
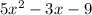
As per the given statement: A polynomial(Q(x)) which, when added to the polynomial
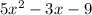 , is equivalent to 0.
, is equivalent to 0.
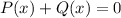
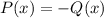
⇒
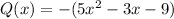
or
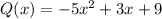
Therefore, the polynomial is,
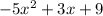
Check:
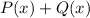 =
=
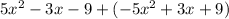
=
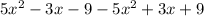
= 0