Answer:
(i) and (iii)
Explanation:
for i)
f(x) =
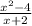
=
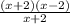
=(x-2)
As x =-2
f(x)=-2-2
f(x)=-4
so it is a continuous function
for ii)
from the result of (i) we can deduce the result of second and we see that it is not equal to zero so it is not a continuous function
iii)
f(x)=
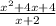
f(x)=
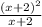
f(x)=
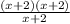
f(x)=x+2
as x= -2
f(x)=-2+2
f(x)=0
so it is a continuous function
iv) From the result of iii we can deduct that
f(x)=0 because it have the same equation so it is not a continuous function