1.
Orbital velocity is the velocity of a satellite with which it goes around a planet in a stable orbit.
We know that orbital velocity is given bu:
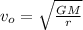
Where, G is the gravitational constant, M is the mass of the planet and r is the distance from the planet.
The orbital velocity is inversely proportional to the distance from the planet i.e. the altitude. Hence, As the altitude above the surface of a planet increases, the orbital velocity decreases.
2.
The tangential velocity is constant as it is tangential to the circular (orbital) path. Orbital velocity is the velocity of a satellite with which it goes around a planet in a stable orbit. Orbital velocity keeps on changing as the direction changes in the circular path. Orbital velocity can be written as the sum of tangential velocity and radial velocity.