Answer:
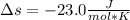
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, since the entropy change when an ideal gas undergo both a volume and temperature change is computed by:
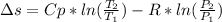
Whereas the molar Cp is 20.786 J/(mol*K) and the final pressure is computed via the Boyle's law:
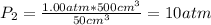
Thus, we plug in the data (temperatures in Kelvin) to obtain:
![\Delta s =20.786(J)/(mol*K) *ln[((-25+273)K)/((25+273)K) ]-8.3145(J)/(mol*K)*ln((10atm)/(1atm) )\\\\\Delta s=-23.0(J)/(mol*K)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/zuc96fa44so0b0pwh1lzkqacdev1ktgjt8.png)
Best regards!