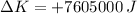Answer:
a) Backward -
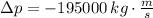 , Forward -
, Forward -
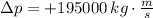 , Directly sideways -
, Directly sideways -
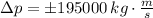 , b) Backward -
, b) Backward -
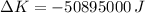 , Forward -
, Forward -
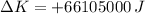 , Directly sideways -
, Directly sideways -
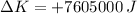 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
a) All scenarios are analyzed by means of the Principle of Momentum Conservation and the Impact Theorem.
Case I - Backward
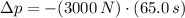
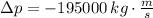
Case II - Forward
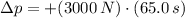
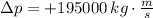
Case III - Directly sideways
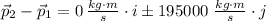
The magnitude of the change of the probe's translational momentum is:
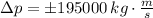
b) The change in kinetic energy is given by the Work-Energy Theorem:
Case I - Backward
The final speed of the probe is:
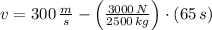
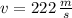
The change in kinetic energy is:
![\Delta K = (1)/(2) \cdot (2500\,kg)\cdot \left[(222\,(m)/(s) )^(2)-(300\,(m)/(s) )^(2) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/middle-school/haomtbml55rrqnp9opahe0hd4fxpz8y361.png)
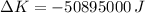
Case II - Forward
The final speed of the probe is:
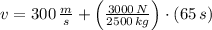
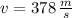
The change in kinetic energy is:
![\Delta K = (1)/(2) \cdot (2500\,kg)\cdot \left[(378\,(m)/(s) )^(2)-(300\,(m)/(s) )^(2) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/middle-school/prnrdh3jwwjjfcq7hr7i5cnowf1e4zlsf3.png)
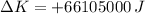
Case III - Directly sideways
The final speed of the probe in the direction perpendicular to the motion line is:
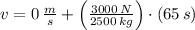
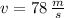
The change in kinetic energy is:
![\Delta K = (1)/(2) \cdot (2500\,kg)\cdot \left[(300\,(m)/(s) )^(2) + (78\,(m)/(s) )^(2) -(300\,(m)/(s) )^(2) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/middle-school/jn328cvyw3dgvfu1sta3bzcpmq7qeg78lo.png)