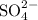Potassium ions and sulfate ions.
Step-by-step explanation
Start with the chemical equation for this reaction.
Sulfuric acid
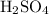 is a strong acid. Potassium hydroxide
is a strong acid. Potassium hydroxide
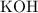 is a strong base. Acids neutralize base in aqueous environments to produce a salt and water.
is a strong base. Acids neutralize base in aqueous environments to produce a salt and water.
That is:
Sulfuric Acid + Potassium Hydroxide → Potassium sulfate + Water
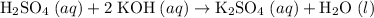
Rewrite the chemical equation as an ionic one. Take all strong electrolytes- including strong acids, strong bases, and soluble salts- apart as their comprising ions. Do not take water molecules apart. As a weak electrolyte, water molecules barely disassociate to produce ions.
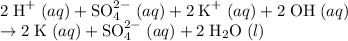
Ions that are present on both sides of the equation by the same quantity do not take part in the net reaction. They are thus considered spectator ions.
- Potassium ions
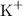
- Sulfate ions