Answer:
Emec = 94050 [J]
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to solve this problem, we must understand that all thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy.
The thermal energy can be calculated by means of the following expression.
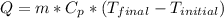
where:
Q = heat [J]
Cp = specific heat of water = 4186 [J/kg*°C]
m = mass = 300 [g] = 0.3 [kg]
T_final = 95 [°C]
T_initial = 20 [°C]
Now we can calculate the heat, replacing the given values:
![Q=0.3*4180*(95-20)\\Q= 94050[J]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/wqydj6e5orzgqpikkmyozcbf85xare52hp.png)
Since all this energy must come from the mechanical energy delivered by the exercise bike, and no energy is lost during the process, the mechanical energy must be equal to the thermal energy.
![Q=E_(mec)\\E_(mec)=94050[J]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/ka1otspwhthagus63l0zxmdxwu8djx8zsf.png)