Answer:
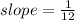
Explanation:
Here is another method to solve your problem. I am showing this method because this is the first method normally taught and a student might not of had the chance yet to learn the other methods
We can solve this problem by using limits and the following function
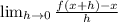
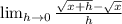
Next multiply by the conjugate of the numerator.
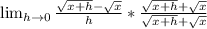
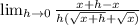
Cancel the x - x
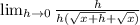
Divide out the h
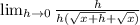
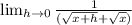
Plugin 0 where h is located
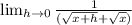
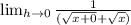
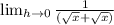
Combine Like terms in denominator
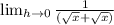
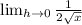
Now lets use our derivative and plugin 36 where x is located and solve
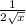
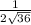
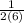
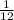
Note, this is a harder method but it is normally the first method taught in Calculus 1.