The perimeter of the rectangle:
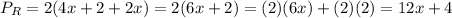
The perimeter of the square:
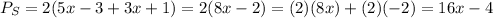
The perimeter of the rectangle is equal to the perimeter of the square. We have the equation:

The side lengths of the square:
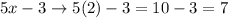
The side lenghts of the rectangle:
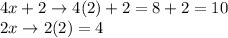
Other method.
If the first figure is a square, then the length of the sides are equal.
Therefore

Further part of the solution as above.