Consider the equation
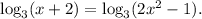
1 step (option 6): rise 3 to the power of left and right sides
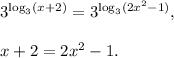
Thus, you get equation from option 5.
2 step (option 2): rewrite the equation in one side
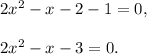
3 step (option 1): factor the previous equation
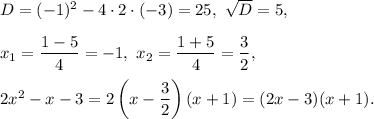
Then the equatios becomes
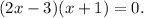
4 step (option 4): If product is equal to zero, then either
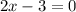 or
or
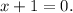
5 step (option 3): Then Potential solutions are −1 and 3/2. You can check them substituting into the initial equation:
for
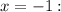
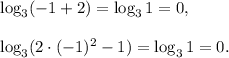
for
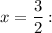
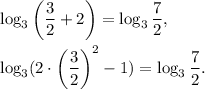
Both are roots.
Answer: correct order of steps is 6, 5, 2, 1, 4, 3.