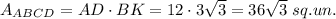1. Consider right triangle ABK. In this triangle AB is the hypotenuse, BK and AK are legs. By the Pythagorean theorem,
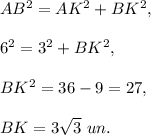
2. Use the definition of
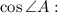
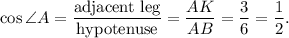
Then
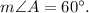
3. Consider right triangle ABD. In this triangle AD is the hypotenuse, AB and BD are legs. Since
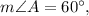 then
then
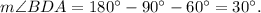
The leg that is opposite to the angle of 30° is half of the hypotenuse, so
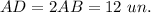
4. The area of parallelogram aBCD is