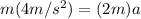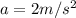Answer:
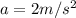
Step-by-step explanation:
As per newton's II law we know that
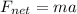
net force on the system of mass is always product of mass and acceleration
So we know that if force on the system of mass is constant then product of mass and acceleration will remain conserved always
here we know that initially mass of the system is "m" and some force is exerted on the system then we have acceleration given as
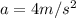
now for the same force if mass is double then we will have