Before solving this question first we have to understand work function.
The work function of a metal is amount of minimum energy required to emit an electron from the surface barrier of metal . Whenever the metal will be exposed to radiation a part of its energy will be utilized to emit an electron while rest will provide kinetic energy to the electron.
Let f is the frequency of incident radiation and f' is the frequency corresponding to work function. Let v is the velocity of the ejected electron.
we know that velocity of an electromagnetic wave is the product of frequency and wavelength. Hence frequency f is given as-
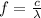
where c is velocity of light and
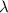 is the wavelength of the wave.
is the wavelength of the wave.
As per the question incident wavelength =313 nm
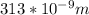 [as 1 nm =10^-9 m]
[as 1 nm =10^-9 m]
The wavelength corresponding to work function is 351 nm i.e
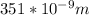
we know that hf=hf'+K.E [ h is the planck's constant whose value is 6.63×10^-34 J-s]
⇒K.E =hf-hf'
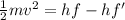
![v^2=(2)/(m) [hf-hf']](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/high-school/x0m488ld4e6hd83xsjaq8zopu0lg0ijk5m.png)
![v^2=(2)/(m) [(hc)/(\lambda) -(hc)/(\lambda ' )]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/high-school/7ngq0cn72dtqjgh995x84e8qvm6tmjgr70.png)
![=(2)/(9.1*10^(-31)kg ) *{6.63*10^(-34) Js *3*10^(8) [(1)/(313*10^(-9) ) -(1)/(351*10^(-9) ) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2019/formulas/physics/high-school/urin6ks69dkrl5ki3j3wcbjy8ma7vn0334.png)
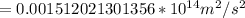
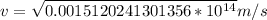
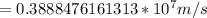
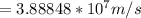 [ans]
[ans]