Answer:
Standard Form Equivalent Form Extreme Values
y=x^2-6x+17 (x-3)^2+8 (3,8)
y=x^2+8x+21 (x+4)^2+5 (-4,5)
y=x^2-16x+60 (x-8)^2-4 (8,-4)
Explanation:
1) Standard form:
y=x^2-6x+17
Equivalent Form:
Can be found using completing the square method.
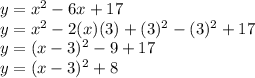
So, Equivalent form is: (x-3)^2+8
Extreme value:
Extreme values are basically the minimum and maximum value of the function.
Minimum Value will be found by finding derivative of the function:
The derivate is: 2x-6
Now, put the derivate equal to zero: 2x-6 = 0
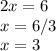
Maximum value can be found by putting minimum value in the given function:
Put x = 3 and solve:
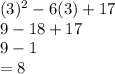
So, the extreme values is: (3,8)
2) Standard form:
y=x^2+8x+21
Equivalent Form:
Can be found using completing the square method.
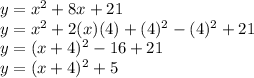
So, Equivalent form is: (x+4)^2+5
Extreme value:
Extreme values are basically the minimum and maximum value of the function.
Minimum Value will be found by finding derivative of the function:
The derivate of x^2+8x+21 is: 2x+8
Now, put the derivate equal to zero:
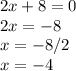
So, minimum value is: -4
Maximum value can be found by putting minimum value in the given function:
Put x = -4 and solve:
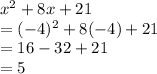
So, Maximum value is: 5
So, the extreme values is: (-4,5)
3) Standard form:
y=x^2-16x+60
Equivalent Form:
Can be found using completing the square method.
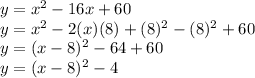
So, Equivalent form is: (x-8)^2-4
Extreme value:
Extreme values are basically the minimum and maximum value of the function.
Minimum Value will be found by finding derivative of the function:
The derivate of x^2-16x+60 is: 2x-16
Now, put the derivate equal to zero:
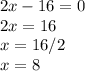
So, minimum value is: 8
Maximum value can be found by putting minimum value in the given function:
Put x = 8 and solve:
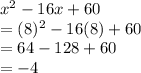
So, Maximum value is: -4
So, the extreme values is: (8,-4)