Given:
No variable equals 1 or 0.
To find:
The statements which is always False.
Solution:
According to identity of multiplication,
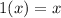
For x=2,
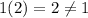
So, the statement
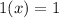 always false because no variable equals 1 or 0.
always false because no variable equals 1 or 0.
Multiplication property of zero,
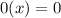
Commutative property of addition,
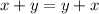
Distributive property of multiplication over addition,
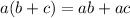
No variable equals 1 or 0. So, all the statements in options B, C, D are always true.
Therefore, the correct option is A.