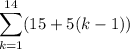11. Derive the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series
Let's call the number of terms
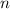 , the first term
, the first term
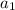 and constant difference
and constant difference
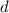
Each term in the series is
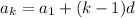
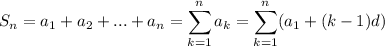
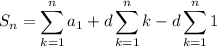
When we sum a constant n times, we're just going to get n times the constant. The sum of the first n natural numbers is n(n+1)/2 as Gauss knew at age eight.
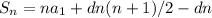
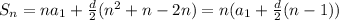
That's a perfectly good formula, but we usually go further by noting
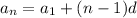
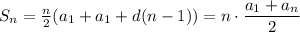
That's n times the average of the first and last element, which makes sense.
12.
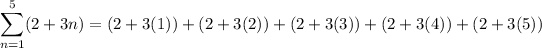
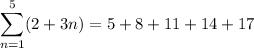
13.
That's a common difference of 3, a first term of 20, and 12 terms
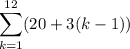
14.
Common difference 5, first term 15, 14 terms