The given chemical equation represents the combustion reaction of propanoic acid:
On balancing we get,
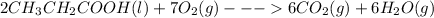
The above balanced chemical equation tells us that, 2 mol
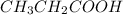 require 7 mol
require 7 mol
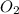 for complete combustion to produce
for complete combustion to produce
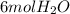 and
and
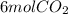
Given moles of
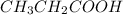 = 1 mol
= 1 mol
Calculating moles of
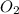 required for combustion:
required for combustion:
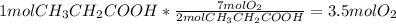
Therefore, 3.5 mol Oxygen is required for complete combustion of 1 mol propanoic acid.