The formula for osmotic pressure is:
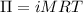
where
 is osmotic pressure,
is osmotic pressure,
 is van't Hoff's factor,
is van't Hoff's factor,
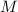 molarity,
molarity,
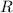 is Ideal gas constant, and T is Temperature.
is Ideal gas constant, and T is Temperature.
 = 132 atm
= 132 atm
The van't Hoff's factor for glucose,
 = 1
= 1
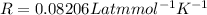
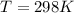
Substituting the values in the above equation we get,
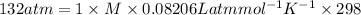
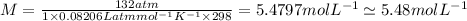
So, the molarity of the solution is
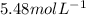 .
.