Answer: 105 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
Gay-Lussac's Law: This law states that pressure is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas at constant volume and number of moles.
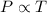 (At constant volume and number of moles)
(At constant volume and number of moles)
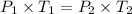
where,
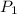 = initial pressure of gas = 50 atm
= initial pressure of gas = 50 atm
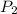 = final pressure of gas = ?
= final pressure of gas = ?
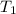 = initial temperature of gas =
= initial temperature of gas =
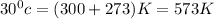
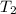 = final temperature of gas =
= final temperature of gas =
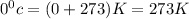
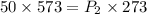
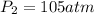
Therefore, the new pressure of the gas will be 105 atm.