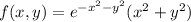
Notice that converting to polar coordinates, setting
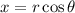
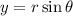
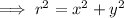
allows us to consider
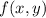
as a function of one variable; let's call it
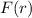
, where
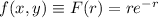
Then
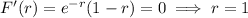
We have
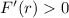
for
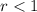
, and
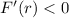
for
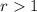
, which means
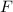
is increasing, then decreasing as

exceeds 1. This suggests that extrema occur for
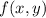
wherever
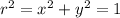
, i.e. along the intersection of the cylinder
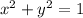
and
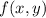
.
Computing the second derivative of
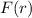
and setting equal to 0 gives
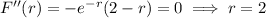
as a possible point of inflection. We have
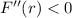
for
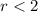
, and namely when
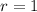
, which means
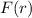
is concave downward around this point. This confirms that
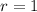
is a site of a maximum. Along this path, we have a maximum value of
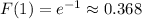
.
Next, to check for possible extrema along the border, we can parameterize
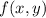
by
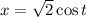
and
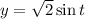
, so that
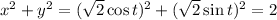
and we can think of
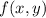
as a function a single variable,
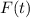
, where
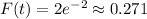
In other words,
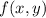
is constant along its boundary
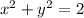
, and this is smaller than the maximum we found before.
So to recap, the maximum value of
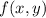
is
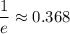
, which is attained along the surface above the circle
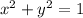
in the
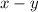
plane.