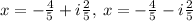Answer:
The solutions to the quadratic equation are:
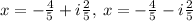
Explanation:
Complex numbers are numbers of the form
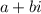 , where
, where
 and
and
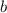 are real numbers.
are real numbers.
For a quadratic equation of the form
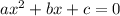 the solutions are
the solutions are
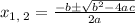
If
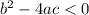 , the equation has two complex solutions that are not real.
, the equation has two complex solutions that are not real.
Quadratic equations with a negative discriminant have no real number solution. However, if we extend our number system to allow complex numbers, quadratic equations will always have a solution.
This quadratic equation
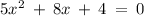 is not factorable, so we apply the quadratic formula.
is not factorable, so we apply the quadratic formula.
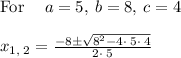
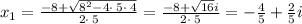
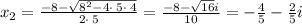
The solutions to the quadratic equation are