Answer: The final velocity of both man and hokey puck will be 0.056 m/s.
Explanation: We are given 2 objects and are undergoing collision. The final velocity of both the objects is same. To calculate the final velocity, we will use the principle of conservation of momentum.
This principle states that when the objects that are colliding makes up a system, then the total momentum will remain constant if no external force is applied on it.
Sum of Initial momentum of two objects = Sum of Final momentum of the two objects
Mathematically,
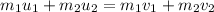 ...(1)
...(1)
where,
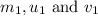 are the mass, initial velocity and final velocity of the first object.
are the mass, initial velocity and final velocity of the first object.
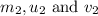 are the mass, initial velocity and final velocity of the second object.
are the mass, initial velocity and final velocity of the second object.
Here, man and hockey puck are moving together after the collision, so their final velocities will be same.
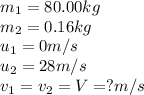
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
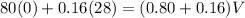
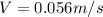
The final velocity of man and hockey puck is 0.056 m/s.