Answer:
Work = 2160 J
Step-by-step explanation:
As per work energy theorem we know that work done is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the cyclist.
As the cyclist is initially moving at speed 8 m/s and after some time his speed changes to 10 m/s
So here we can say that
final kinetic energy - initial kinetic energy = work done
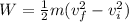
now by plug in all values
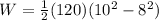
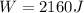
so work done by cyclist will be 2160 J