Answer:
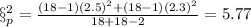
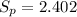
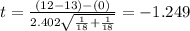
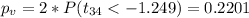
Step-by-step explanation:
When we have two independent samples from two normal distributions with equal variances we are assuming that
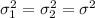
And the statistic is given by this formula:
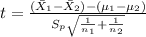
Where t follows a t distribution with
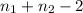 degrees of freedom and the pooled variance
degrees of freedom and the pooled variance
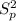 is given by this formula:
is given by this formula:
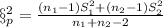
This last one is an unbiased estimator of the common variance
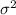
The system of hypothesis on this case are:
Null hypothesis:
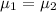
Alternative hypothesis:
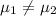
Or equivalently:
Null hypothesis:
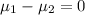
Alternative hypothesis:
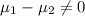
Our notation on this case :
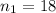 represent the sample size for group 1
represent the sample size for group 1
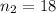 represent the sample size for group 2
represent the sample size for group 2
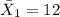 represent the sample mean for the group 1
represent the sample mean for the group 1
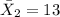 represent the sample mean for the group 2
represent the sample mean for the group 2
 represent the sample standard deviation for group 1
represent the sample standard deviation for group 1
 represent the sample standard deviation for group 2
represent the sample standard deviation for group 2
First we can begin finding the pooled variance:
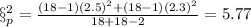
And the deviation would be just the square root of the variance:
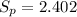
And now we can calculate the statistic:
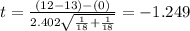
Now we can calculate the degrees of freedom given by:
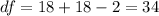
And now we can calculate the p value using the altenative hypothesis:
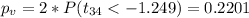
If we compare the p value obtained and using the significance level assumed
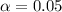 we have
we have
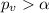 so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis.
so we can conclude that we have enough evidence to FAIL to reject the null hypothesis.