Answer:
20.94 m/s, 235.44 Pa
Step-by-step explanation:
Acceleration due to gravity g =
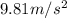
height h = 0.024 m
From density of air = P/RT
= (98000)/(287 * 318.14) =
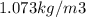
Using Bernoulli equation
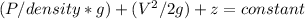
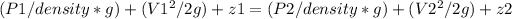
Here z1 = z2 (since the outlets have the same differential height) and V2 = 0 (no velocity at the tip)
Solving and making V1 subject of the formula
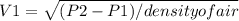
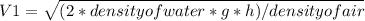

= 20.94 m/s
Change in pressure P2 - P1= density of water * g * height
= 1000*9.81*0.024
=235.44 Pa