To solve this problem it is necessary to apply the concepts related to temperature stagnation and adiabatic pressure in a system.
The stagnation temperature can be defined as
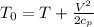
Where
T = Static temperature
V = Velocity of Fluid
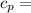 Specific Heat
Specific Heat
Re-arrange to find the static temperature we have that
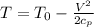
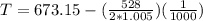
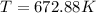
Now the pressure of helium by using the Adiabatic pressure temperature is
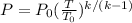
Where,
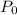 = Stagnation pressure of the fluid
= Stagnation pressure of the fluid
k = Specific heat ratio
Replacing we have that
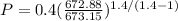
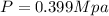
Therefore the static temperature of air at given conditions is 72.88K and the static pressure is 0.399Mpa
Note: I took the exactly temperature of 400 ° C the equivalent of 673.15K. The approach given in the 600K statement could be inaccurate.