To solve this problem it is necessary to apply the concepts related to energy conservation.
In this case the kinetic energy is given as
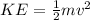
Where,
m = mass
v= Velocity
In the case of heat lost energy (for all 4 wheels) we have to
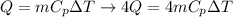
m = mass
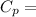 Specific Heat
Specific Heat
 = Change at temperature
= Change at temperature
For conservation we have to
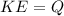
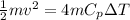
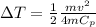
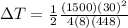
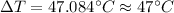
Therefore the temperature rises in each of the four brake drums around to 47°C