Answer:
145.52137 m/s
1.4 m
0.7 m
60.6339 Hz
121.2678 Hz
Step-by-step explanation:
T = Tension = 120 N
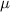 = Linear density =
= Linear density =
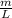
m = Mass of wire = 6.8 g
L = Length of wire = 1.2 m
n = Number of loops
Velocity is given by
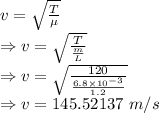
The speed of waves on the wire is 145.52137 m/s
Wavelength is given by
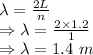
The wavelength of the waves that produces one-loop standing waves is 1.4 m
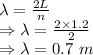
The wavelength of the waves that produces two-loop standing waves is 0.7 m
Frequency is given by
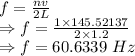
The frequency of the waves that produces one-loop standing waves is 60.6339 Hz
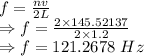
The frequency of the waves that produces two-loop standing waves is 121.2678 Hz