The question has incomplete information. The pH values are not discriminated. Let's do, as an example, to pH = 4.69.
Answer:
For pH = 4.69, [C₆H₅NH₂]/[C₆H₅NH₃⁺] = 0.708
Step-by-step explanation:
C₆H₅NH₂ is a base, and, when in aqueous solution, forms a conjugate acid, which is C₆H₅NH₃⁺. The equilibrium between these two species makes a buffer, a solution that prevents the change in pH by the addition of base or acid.
The pH of a buffer can be calculated by the equation of Handerson-Halsebach:
pH = pKa + log[conjugate base]/[acid]
Where pKa = -logKa, and Ka is the equilibrium constant of the acid. For the base, the equilibrium constant, Kb, is equal to 7x10⁻¹⁰, and
Ka*Kb = Kw
Where Kw is the equilibrium constant for water 1.00x10⁻¹⁴, so Ka for the conjugate acid is:
Ka = 1.00x10⁻¹⁴/7.00x10⁻¹⁰
Ka = 1.43x10⁻⁵
pKa = 4.84
pH = 4.84 + log [C₆H₅NH₂]/[C₆H₅NH₃⁺] (By this step, the pH values given by the question must be substituted)
4.69 = 4.84 + log[C₆H₅NH₂]/[C₆H₅NH₃⁺]
log[C₆H₅NH₂]/[C₆H₅NH₃⁺] = - 0.15
[C₆H₅NH₂]/[C₆H₅NH₃⁺] =
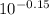
[C₆H₅NH₂]/[C₆H₅NH₃⁺] = 0.708