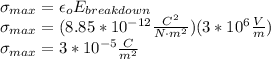Answer:
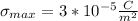
Step-by-step explanation:
The electric field on the surface of a conductor is given by:
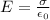
Here
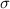 is the surface charge density and
is the surface charge density and
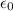 the permittivity of free space. Thus, the highest surface charge density that can exist in a conductor is given by the value of the dielectric breakdown of the air multiplied by the permittivity of free space:
the permittivity of free space. Thus, the highest surface charge density that can exist in a conductor is given by the value of the dielectric breakdown of the air multiplied by the permittivity of free space: