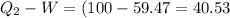Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Efficiency of the electric power plant is
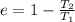
Here Temperature of hot source
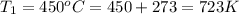
and Temperature of sink
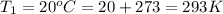
Hence the efficiency is
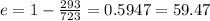
Now another formula for thermal efficiency Is
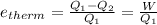
Here QI is the of heat taken from source 100 MJ ; Q2 of heat transferred to the sink (river) to be found
W is the of work done and W = QI -Q2
Hence From
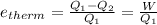
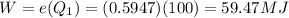
Hence the of heat transferred to the river Is