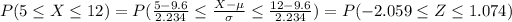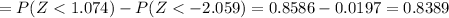Answer:
a)
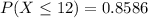
b)
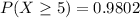
c)
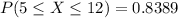
Explanation:
The binomial distribution is a "DISCRETE probability distribution that summarizes the probability that a value will take one of two independent values under a given set of parameters. The assumptions for the binomial distribution are that there is only one outcome for each trial, each trial has the same probability of success, and each trial is mutually exclusive, or independent of each other".
Let X the random variable of interest, on this case we now that:
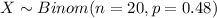
The probability mass function for the Binomial distribution is given as:
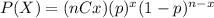
Where (nCx) means combinatory and it's given by this formula:
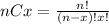
We need to check the conditions in order to use the normal approximation.
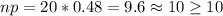

So we see that we satisfy the conditions and then we can apply the approximation.
If we appply the approximation the new mean and standard deviation are:
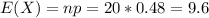
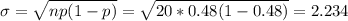
Part a
We want this probability:
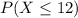
We can use the z score given by this formula
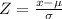 .
.
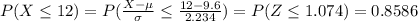
Part b
We want this probability:
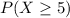
We can use again the z score formula and we have:
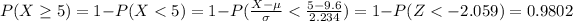
Part c
We want this probability: