To solve this problem it is necessary to apply the concepts related to the heat exchange of a body.
By definition heat exchange in terms of mass flow can be expressed as
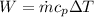
Where
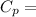 Specific heat
Specific heat
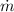 = Mass flow rate
= Mass flow rate
 = Change in Temperature
= Change in Temperature
Our values are given as
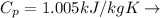 Specific heat of air
Specific heat of air
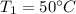
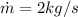
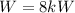
From our equation we have that
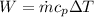
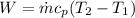
Rearrange to find
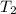
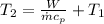
Replacing
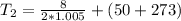
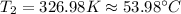
Therefore the exit temperature of air is 53.98°C