Answer:
The Domain D = {y ∈ R / y ≠
 y ≠ 0}
y ≠ 0}
Explanation:
Let ,
f(y) =
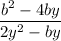 -
-
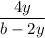
The above function would be defined only when the denominator of anyone or both the terms of the function do not become 0 -
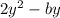 ≠ 0 and b - 2y ≠ 0
≠ 0 and b - 2y ≠ 0
∴ y(2y - b) ≠ 0 and y ≠

Either y ≠ 0 or y ≠

∵ The domain of a function consists of only those points where the function is defined -
The Domain D consists of all y ∈ Real numbers such that y ≠ 0 and y ≠
