Answer:
90 mg of H₂O
Step-by-step explanation:
The reaction that takes place is:
2HCl + Ba(OH)₂ → BaCl₂(aq) + 2H₂O
With the information given by the problem and the definition of molarity (M=n/V), we can calculate the moles of HCl:
20.00 mL * 0.250 M = 5 mmol HCl
Now we use the stoichiometric ratio to convert moles of HCl to moles of H₂O and then to mass of H₂O:
5 mmol HCl *
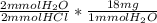 = 90 mg H₂O
= 90 mg H₂O