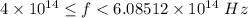Answer:
0.7515875 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
f = Maximum frequency =
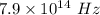
h = Planck's constant =
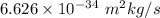
W = Work function = 2.52 eV
Converting to Joules
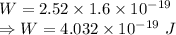
Maximum photon energy is given by
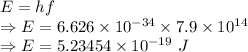
Maximum Kinetic energy is given by
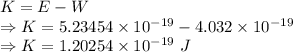
Converting to eV
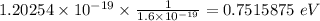
The maximum kinetic energy of electrons ejected from this surface is 0.7515875 eV
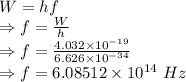
The range of frequencies for which no electrons are ejected is