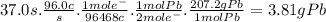Answer:
3.81 g Pb
Step-by-step explanation:
When a lead acid car battery is recharged, the following half-reactions take place:
Cathode: PbSO₄(s) + H⁺ (aq) + 2e⁻ → Pb(s) + HSO₄⁻(aq)
Anode: PbSO₄(s) + 2 H₂O(l) → PbO₂(s) + HSO₄⁻(aq) + 3H⁺ (aq) + 2e⁻
We can establish the following relations:
- 1 A = 1 c/s
- 1 mole of Pb(s) is deposited when 2 moles of e⁻ circulate.
- The molar mass of Pb is 207.2 g/mol
- 1 mol of e⁻ has a charge of 96468 c (Faraday's constant)
Suppose a current of 96.0A is fed into a car battery for 37.0 seconds. The mass of lead deposited is: