Answer : The enthalpy of combustion per mole of
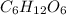 is -2815.8 kJ/mol
is -2815.8 kJ/mol
Explanation :
Enthalpy change : It is defined as the difference in enthalpies of all the product and the reactants each multiplied with their respective number of moles. It is represented as
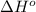
The equation used to calculate enthalpy change is of a reaction is:
![\Delta H^o_(rxn)=\sum [n* \Delta H^o_f(product)]-\sum [n* \Delta H^o_f(reactant)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/2s3ruq22efwpgh8t0j30g9r9s637g4eoxq.png)
The equilibrium reaction follows:
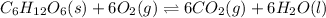
The equation for the enthalpy change of the above reaction is:
![\Delta H^o_(rxn)=[(n_((CO_2))* \Delta H^o_f_((CO_2)))+(n_((H_2O))* \Delta H^o_f_((H_2O)))]-[(n_{(C_6H_(12)O_6)}* \Delta H^o_f_{(C_6H_(12)O_6)})+(n_((O_2))* \Delta H^o_f_((O_2)))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/5ln5jibrlwh5rr0of60xyz1og20byo2qrz.png)
We are given:
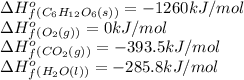
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\Delta H^o_(rxn)=[(6* -393.5)+(6* -285.8)]-[(1* -1260)+(6* 0)]=-2815.8kJ/mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/39tz8ryxwhv02nsjp632iunz68sh2352f8.png)
Therefore, the enthalpy of combustion per mole of
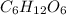 is -2815.8 kJ/mol
is -2815.8 kJ/mol