Answers:
a)
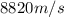
b)
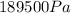
Step-by-step explanation:
We have the following data:
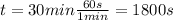 is the time
is the time
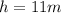 is the height the water reaches vertically
is the height the water reaches vertically
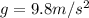 is the acceleration due gravity
is the acceleration due gravity
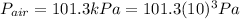 is the pressure of air
is the pressure of air
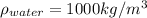 is the density of water
is the density of water
Knowing this, let's begin:
a) Initial speed of water
Here we will use the following equation:
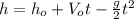 (1)
(1)
Where:
 is the initial height of water
is the initial height of water
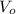 is the initial speed of water
is the initial speed of water
Isolating
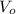 :
:
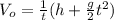 (2)
(2)
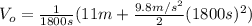
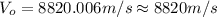 (3)
(3)
b) Pressure in the chamber
In this part we will use the following equation:
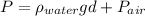 (4)
(4)
Where:
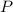 is the absolute pressure in the chamber
is the absolute pressure in the chamber
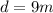 is the depth
is the depth
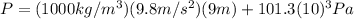
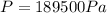 (5)
(5)