Answer: The mass of methane burned is 12.4 grams.
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation for the combustion of methane follows:
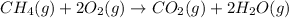
The equation for the enthalpy change of the above reaction is:
![\Delta H^o_(rxn)=[(1* \Delta H^o_f_((CO_2(g))))+(2* \Delta H^o_f_((H_2O(g))))]-[(1* \Delta H^o_f_((CH_4(g))))+(2* \Delta H^o_f_((O_2(g))))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/7v9r88v18llus1oi9rh2rbdqg9fl65g1gj.png)
We are given:
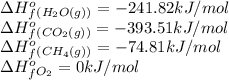
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\Delta H^o_(rxn)=[(1* (-393.51))+(2* (-241.82))]-[(1* (-74.81))+(2* (0))]\\\\\Delta H^o_(rxn)=-802.34kJ](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/rnekf5ssolbzxzjtb3bfrdmbtv7xdg5oj0.png)
The heat calculated above is the heat released for 1 mole of methane.
The process involved in this problem are:
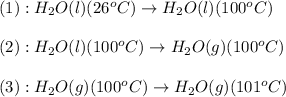
Now, we calculate the amount of heat released or absorbed in all the processes.
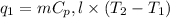
where,
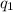 = amount of heat absorbed = ?
= amount of heat absorbed = ?
m = mass of water = 242.0 g
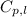 = specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g°C
= specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g°C
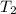 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
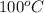
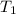 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
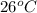
Putting all the values in above equation, we get:
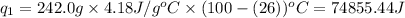
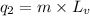
where,
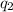 = amount of heat absorbed = ?
= amount of heat absorbed = ?
m = mass of water or steam = 242 g
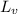 = latent heat of vaporization = 2257 J/g
= latent heat of vaporization = 2257 J/g
Putting all the values in above equation, we get:
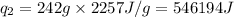
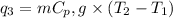
where,
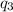 = amount of heat absorbed = ?
= amount of heat absorbed = ?
m = mass of steam = 242.0 g
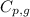 = specific heat of steam = 2.08 J/g°C
= specific heat of steam = 2.08 J/g°C
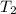 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
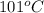
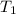 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
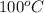
Putting all the values in above equation, we get:
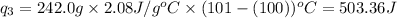
Total heat required =
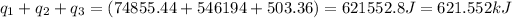
- To calculate the number of moles of methane, we apply unitary method:
When 802.34 kJ of heat is needed, the amount of methane combusted is 1 mole
So, when 621.552 kJ of heat is needed, the amount of methane combusted will be =
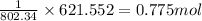
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
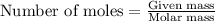
Molar mass of methane = 16 g/mol
Moles of methane = 0.775 moles
Putting values in above equation, we get:

Hence, the mass of methane burned is 12.4 grams.