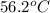Answer : The final temperature of the aluminum and ethylene glycol is
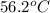
Explanation :
In this problem we assumed that heat given by the hot body is equal to the heat taken by the cold body.
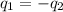
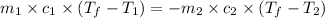
where,
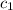 = specific heat of aluminum =
= specific heat of aluminum =
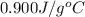
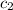 = specific heat of ethylene glycol =
= specific heat of ethylene glycol =
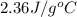
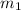 = mass of aluminum = 13.60 g
= mass of aluminum = 13.60 g
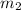 = mass of ethylene glycol = 23.27 g
= mass of ethylene glycol = 23.27 g
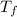 = final temperature of aluminum and ethylene glycol = ?
= final temperature of aluminum and ethylene glycol = ?
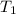 = initial temperature of aluminium =
= initial temperature of aluminium =
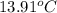
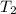 = initial temperature of ethylene glycol =
= initial temperature of ethylene glycol =
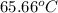
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
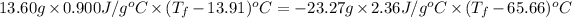
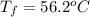
Therefore, the final temperature of the aluminum and ethylene glycol is