Step-by-step explanation:
Relation between density, height, and surface tension is as follows.
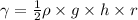
The given data is as follows.
Density, (
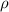 ) = 998.2
) = 998.2
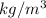
g = 9.807 m/s
h = 4.96 cm =
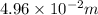 (as 1 m = 100 cm)
(as 1 m = 100 cm)
r = 0.3 mm =
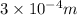 (as 1 m = 10000 mm)
(as 1 m = 10000 mm)
Therefore, putting the given values into the above formula and calculate the surface tension as follows.
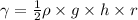
=
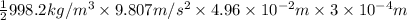
=
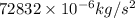
or, =
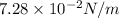
Thus, we can conclude that value of surface tension is
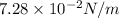 .
.